Additive manufacturing services, also known as 3D printing technology, are transforming the manufacturing industry with their numerous advantages. The technology enables industries to create complex designs and parts, leading to a surge in demand for these services. Moreover, additive manufacturing services offer reduced manufacturing time and cost, resulting in faster production, less material waste, and the ability to create more intricate designs. This also facilitates customization and personalization of products, particularly in the healthcare, aerospace, and automotive industries.

Additive manufacturing services are particularly relevant in the healthcare sector, where there is a growing demand for customized and affordable medical devices. Governments worldwide are investing in additive manufacturing services to enhance their manufacturing capabilities and stay competitive in the global market. This has resulted in the growth of the additive manufacturing services market in various countries.
The aerospace and defense sector is also a significant user of additive manufacturing services, especially for the production of lightweight and complex parts. With the expansion of this sector, there is an increasing demand for additive manufacturing services. , offering various benefits and advantages to industries and consumers alike.
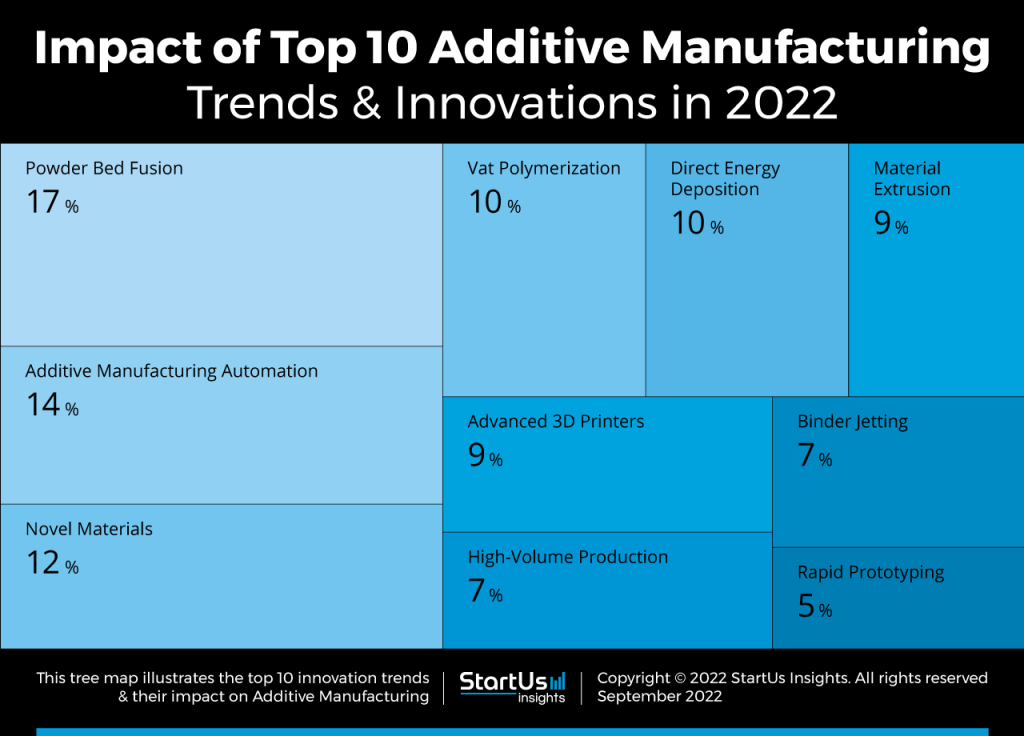
Top 10 Additive Manufacturing Trends in 2023
1. Powder Bed Fusion
Powder bed fusion (PBF) 3D printing is a popular technology used to create low-volume functional parts with mechanical properties comparable to machining and casting. PBF supports a wide range of materials and enables the simultaneous development of multiple parts, making it suitable for printing machine parts, jigs, fixtures, and other components. The most common PBF methods are selective laser sintering (SLS), electron beam melting, and selective laser melting (SLM). Recent advancements in the field have focused on improving powder purity and reducing size distribution, which has accelerated PBF’s applications. Moreover, startups are developing low-cost 3D printing materials to make PBF more affordable and accessible.
Aixway3D offers Industrial Micron 3D Metal Printing
Aixway3D, a Chinese startup, has created Precision-100, an industrial micron 3D metal printer. It features ultra-fine metal powder bed, proprietary feeding technology, and a highly accurate laser, providing an accuracy of 2 to 5 microns. The 3D printer supports complex structures and offers ultra-low surface roughness, eliminating the need for additional post-processing techniques.
3DPS provides On-Demand Selective Laser Sintering
3DPS is a Singaporean startup that prints parts for manufacturers with 1 mm minimum wall thickness and 0.2 mm dimensional accuracy. This allows manufacturers to develop functional parts, assemblies, and nylon components with complex geometries and robust mechanical properties.
2. Additive Manufacturing Automation
Additive manufacturing automation streamlines 3D printing lines using digital workflows and automation systems to increase production throughput. Startups offer printer-agnostic software and hardware solutions to automate part processing, enhance print flexibility, and minimize waste. Automated 3D printing lines reduce labor costs and eliminate manual errors.
AM-Flow advances Automated Industrial 3D Printing:
AM-Flow, a Dutch startup, offers an automated industrial 3D printing ecosystem that integrates hardware and software solutions to automate manufacturing and associated processes. It combines digital manufacturing, automated sorting, robotic part handling, and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to automate entire production workflows and integrate lean principles for manufacturers leveraging additive manufacturing.
Printinue enables Continuous Printing:
Printinue, a German startup, offers an automated 3D printer for continuous printing that enables the serial production of high-quality products and parts. It automates production and quality control, allowing manufacturers to create components with complex geometries at low costs while ensuring efficient and sustainable operations.
3. Novel Materials
Startups are developing novel materials to expand additive manufacturing applications in various fields. Smart materials, ceramics, electronics, biomaterials, and composites enable the 3D printing of unconventional products like medical devices, consumer electronics, and bioartificial organs. Additionally, high-value 3D printable materials are extracted from waste streams to reduce virgin material requirements and emissions.
f3nice provides Additive Manufacturing Feedstock
f3nice, an Italian startup, produces high-quality metal powders for additive manufacturing by recycling valuable metals such as steel and other alloys. They offer different size ranges based on customer requirements and adopt a circular approach to feedstock production, improving sustainability in metal 3D printing.
Foundation Alloy provides Novel Alloys
Foundation Alloy, a US-based startup, produces innovative alloys for 3D printing. Their material design and vertically integrated approach boost production capacity, efficiency, flexibility, and reduce energy consumption while enabling faster metal part production.
4. Vat Polymerization
Vat photopolymerization (VPP) is a fast and old 3D printing process that sees innovations. Projection and continuous stereolithography are widely used in various industries. Volumetric stereolithography will improve resolution and processing for faster development. VPP allows quick production of polymer components with smooth finish and quality. Startups are developing cost-effective resins, materials, and post-processing solutions to expand VPP’s use cases.
RAYSHAPE advances Direct Light Processing (DLP)
UK startup RAYSHAPE creates industrial and dental 3D printers using DLP technology. Their Shape1+ Series features a high-precision linear guide and optical system for uniform light output, while the Shape1+ Dental produces dental models and clear aligners. Both printers offer accurate layer thickness and high surface quality.
Masitte makes Laser SLA 3D Printers
Chinese startup Masitte provides compact laser SLA 3D printers for large-scale production, such as the Masitte Large. The printers feature an all-aluminum frame and F-theta scan lens, allowing manufacturers to produce accurate and consistent parts for prototyping and mass production. Masitte also offers printers for the jewelry, dental, and footwear industries.
5. Direct Energy Deposition
DED 3D printing uses beams such as electron beams and wire arcs to create metal parts with high precision and a range of materials. It allows for specific part requirements, reduces wastage and finds use in maintenance and near-net-shape part production.
Alloy Additive offers Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM)
Alloy Additive is a Turkish startup that offers metal parts made using the WAAM method. Its robotic system supports alloys like stainless steel, Ti64, and Inconel625 and features a large print area. The solution enables near-net shape manufacturing of new and out-of-production parts on-demand and on-site.
SBI furthers Plasma Metal Deposition
Austrian startup SBI utilizes plasma metal deposition to develop parts for thermosphere applications at low costs. Its 3D printer, M3DP, combines plasma welding with proprietary control systems, and supports various metals like steel and titanium. It also features a 0.5 to 10 kg/h deposition rate and 0.7 to 3 mm layer thickness.
6. Material Extrusion
Material extrusion, the most economical additive manufacturing process, utilizes Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and is widely used in construction and small-scale production runs. Startups are enhancing FDM’s nozzle radius limits to achieve high-precision, accelerating prototype development and design finalization.
NematX offers High-Performance 3D Printing
NematX, a Swiss startup, offers Nematic 3D Printing, a proprietary technology that uses liquid crystal polymer (LCP) to reinforce polymer matrices for high inertness, fire resistance, and recyclability. It finds use in aerospace, medical, and electronics manufacturing.
Karkhana.io delivers an FDM 3D Printing Service
Karkhana.io is an Indian startup that provides an FDM 3D printing service for the automotive, aerospace, and robotics industries. The startup’s web interface allows manufacturers to upload part designs and choose the material required for production. It supports polycarbonate, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG), and polylactic acid (PLA). By leveraging Karkhana.io’s service, manufacturers are able to enable on-demand production and accelerate time to market.
7. Advanced 3D Printers
Innovations in materials expand the potential uses of additive manufacturing, but the technology’s performance currently limits adoption. Startups are addressing this by offering tailored 3D printers for specific use cases, improving printer movement and energy efficiency, and reducing costs to improve market penetration.
Brinter creates a Modular Bioprinter
Finnish startup Brinter develops a modular bioprinter for medical, pharma, and life sciences industries that supports a range of bioinks and various print surfaces. Its companion software simplifies printer management, and the bioprinter features optional built-in UV/visible light LEDs for disinfection. It allows researchers to print cancer models, body parts, organs, and personalized drugs.
Verde Mantis provides an Easy-to-Use Desktop 3D Printer
Verde Mantis is a US startup that offers an easy-to-use desktop 3D printer equipped with a Raspberry Pi module, a magnetic bed, a self-leveling platform, and an in-built camera. It supports a plug-and-play mode, simplifying 3D printer control, and making additive manufacturing more accessible for creators.
8. High-Volume Production
3D printing is ideal for low-volume, high-mix manufacturing, but traditional methods have limitations for mass production. Advances in materials, 3D printers, and automation software make it possible to use 3D printing for high-volume production and outsource workflows to smart factories, enabling on-demand, agile production at a lower cost.
Q.big 3D enables Large and High-Volume 3D Printing
Q.big 3D, a German startup, provides QUEEN 1, a high-volume 3D printer that uses variable fused granular fabrication (VFGF) technology. With a 1.7×1.1×1.05-meter installation size and high printing speed, it supports serial production and a large selection of polymer granulates, enabling manufacturers in the automotive, agriculture machinery, and medical device industries to mass-produce large parts.
Phasio furthers Decentralized Manufacturing
Singaporean startup Phasio develops a software solution for additive manufacturing service providers. The software streamlines operations across various production floors and allows for decentralized manufacturing. Phasio’s software automates order processing, instant quoting, payments, shipping, and accounting, enabling service providers to set up a digital storefront and increase productivity.
9. Binder Jetting
Binder jetting additive manufacturing supports ceramic, polymer, and metal feedstocks, making it ideal for casting molds and high-fidelity prototyping. Although it produces high-precision parts cost-effectively, the mechanical properties of parts cannot match those made by PBF. Nonetheless, improvements in binders and feedstock powders expand its applications.
SFS develops Sand Binder Jetting 3D Printers
South Korean startup SFS develops Freeforms P1000 and P2000, sand binder jet 3D printers that produce casting molds, cores, and injection molds by combining an inorganic binder and casting sand powders. The non-toxic and environmentally friendly binder allows for mold development in shipbuilding, automotive, and power equipment manufacturing.
Freeform Composites makes 3D Printable Carbon Composites
Australian startup Freeform Composites develops 3D printable carbon composites with high-performance and light-weight features. Its technology eliminates the need for tooling and fixtures, reducing lead times and cost. Aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturers use it to print high-performance components.
10. Rapid Prototyping
Startups provide high-performance 3D printers and design software to speed up prototype development, aiding the acceleration of design revision and product finalization without tool development. Rapid prototyping eliminates manual labor and errors.
SmartZavod makes an Automated 3D Printer
SmartZavod is a Ukrainian startup offering an automated 3D printer, SmartZavod CEH #1, for rapid prototyping. Users can access the printer through a web platform or purchase it outright. The printer is also remotely configurable and controllable and includes an automatic part removal system. This makes it convenient for designers to utilize SmartZavod’s 3D printers and speed up their prototyping processes.
e3Dify Designs creates an Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled FDM Printer
Indian startup e3Dify Designs offers Arctic 3D Printer, an IoT-enabled FDM printer with dual-layer cooling fan, swappable nozzles, automated filament loading/unloading, high build volume, and filament runout detection. It enables rapid prototyping and faster product development cycles for designers and manufacturers.
Source: Startus Insights
