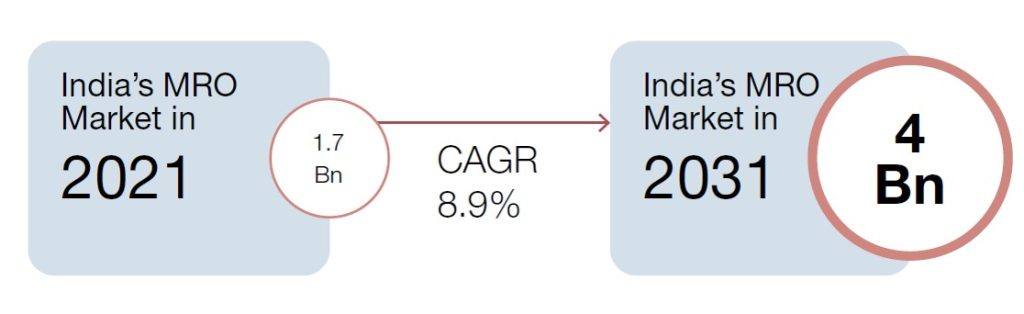
The aerospace industry heavily relies on Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) to ensure aircraft safety, reliability, and availability. The demand for MRO services has been on the rise due to an increase in air travel and aging aircraft. India’s aviation industry is set to become the third-largest buyer of commercial planes after the US and China, with a fleet size of over 713 aircraft and plans to add more in the near future. As a result, the Indian aerospace industry is one of the fastest-growing markets worldwide. The Indian MRO industry is still in its early stages, with a current size of USD 1.7 billion as of 2021, but is expected to reach USD 4.0 billion by 2031. Rising consumer demand, favourable policies, and labour arbitrage are some of the factors that could fuel the industry’s growth. Additionally, redelivery maintenance contracts can help drive desired capacity expansion.

However, the Indian MRO industry faces challenges breaking into existing value chains involving OEMs, globally established MROs, and airline operators. Other obstacles include implementing offset clauses, accessing credit, infrastructure availability, licensing and certification, taxes/duties, and land lease rentals. The government has initiated various reforms to develop India as a global MRO hub. Incremental steps such as joint ventures focus on lower IP control MRO segments and a gradual shift towards higher-end value chains are recommended.

Moreover, the increasing complexity of aircraft systems and regulatory pressures pose significant challenges to the MRO industry. Nonetheless, developing a sustainable end-to-end ecosystem for commercial, general, and military MRO activities could provide benefits such as a reduction in foreign exchange outflow, greater employment opportunities, and domestic MRO capability augmentation. Additionally, airline operators could enjoy lower MRO costs, reduced turnaround time, and less inventory. This study aims to explore various aspects that influence the MRO ecosystem in India, identify challenges faced by stakeholders, and propose a roadmap for near and long-term developments in the sector.
Regulatory Environment
The Government of India has implemented various policies and regulations to elevate India’s MRO sector to global standards, with the goal of establishing the country as a premier MRO hub. These initiatives include incentivizing companies to establish MROs in India by reducing the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on domestic MRO services from 18% to 5% with full Input Tax Credit as of April 1, 2020, and treating transactions sub-contracted by foreign OEMs and MRO companies to domestic MROs as exports with zero-rated GST. Additionally, custom duty on tools, toolkits, and spares imported by MROs has been waived, and 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) through the automatic route has been permitted.
To encourage more investments, the Ministry of Civil Aviation introduced a new MRO Policy in 2021, including key reform measures such as land leasing through open tenders and eliminating the AAI’s royalty. Moreover, land allotment for establishing MRO facilities is expected to be for 30 years instead of the current short-term period of 3-5 years. These policies and regulations have been formulated to facilitate strategic and systemic advancements, aiming to establish India as a global MRO hub.
Trends in MRO
One of the key trends in the MRO industry is the increasing use of technology. Digitalization has revolutionized the way MRO is carried out, with the use of advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. These technologies have enabled predictive maintenance, allowing MRO teams to identify potential issues before they occur and take preventive measures. This has resulted in reduced downtime, improved safety, and increased efficiency.
Another trend in the MRO industry is the growing adoption of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing. This technology enables the production of complex parts and components with higher precision and accuracy, which is particularly useful in the aerospace industry where parts can be difficult to source. Additive manufacturing can also reduce lead times and costs, making it a popular choice for MRO providers.
Challenges in MRO
The MRO industry faces several challenges, one of which is the increasing complexity of aircraft systems. Modern aircraft are equipped with sophisticated systems and components that require specialized expertise to maintain and repair. As a result, MRO providers need to invest in training and upskilling their workforce to ensure they have the necessary skills and knowledge to work on these systems.
Another challenge is regulatory pressures. The aerospace industry is heavily regulated, and MRO providers must comply with numerous regulations and standards. Failure to comply can result in fines, penalties, and loss of reputation. Keeping up with regulatory changes and requirements can be a significant challenge for MRO providers, particularly smaller companies with limited resources.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the MRO market in the aerospace industry is growing, driven by increasing demand for air travel and the need to maintain aging aircraft. However, the industry also faces significant challenges, such as increasing complexity of aircraft systems and regulatory pressures. MRO providers must invest in technology and upskilling their workforce to remain competitive and meet the changing needs of the industry. In addition, collaboration and partnership between MRO providers, airlines, and OEMs can help address some of the challenges facing the industry and ensure a safe and reliable air transport system.
Sources:
- Bureau of Research on Industry and Economic Fundamentals Pvt. Ltd
- Aviation Business News
- Centre for Aviation
